- HOME
- POLICY AREA
- Consumer Policy
- Consumer Policy
Consumer Policy
Overview
Principles of Consumer Policy
Consumer policy is a process of direct and indirect government interventions, through the enforcement of laws and regulations, aimed at resolving consumer issues in the market economy. The paradigm of consumer policy has shifted from “consumer protection,” focusing on protecting consumers in a weaker position, to “consumer sovereignty,” putting emphasis on supporting consumers to be able to resolve issues on their own.
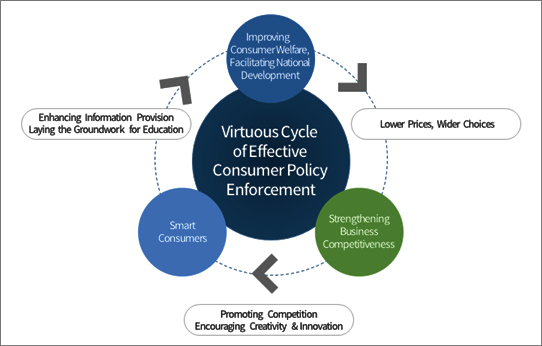
Effective consumer policies, which enhance the capability of consumers, serve as the basis for the virtuous cycle of promoting consumer welfare and increasing competitive pressure among businesses. Increased competitive pressure leads businesses to innovate and lower prices.
Virtuous Cycle of Effective Consumer Policy Enforcement
A Shift in Paradigm of Consumer Policy
1) The Establishment of Consumer Policy Implementation System
The fully revised Consumer Protection Act (promulgated on Sep. 27, 2006) and the fully revised Enforcement Decree of the Consumer Protection Act (promulgated on Mar. 27, 2007) were enforced on March 28, 2007. The government reorganization in February 2008 introduced a unified implementation system for consumer policies.
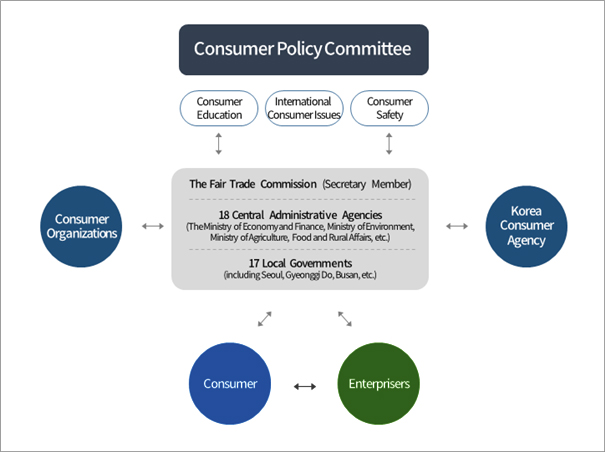
As a result, the powers to establish and review consumer policy plans, operate the Consumer Policy Committee (hereinafter referred to as “the Committee”), and enact and amend the Framework Act on Consumers (hereinafter referred to as “the Framework Act”), the Product Liability Act, and the Consumer Cooperatives Act were transferred from the old Ministry of Finance and Economy to the Korea Fair Trade Commission (“the KFTC”). Also the Korea Consumer Protection Agency was renamed as the Korea Consumer Agency (hereinafter referred to as “the KCA”) and the KFTC took over the power to govern the agency in March 2007.
The chairperson of the KFTC serves as the secretary member of the Committee who is in charge of the efficient operation of the Committee. The Committee is a committee established under the jurisdiction of the Prime Minister in order to consolidate, coordinate, deliberate, and resolve fundamental policies concerning the enhancement of consumers’ rights and interests and the improvement of consumers’ lives.
This paradigm shift was aimed at strengthening the position of consumers as the ones who exercise sovereignty, not just as the subjects of protection.
Consumer Policy Implementation System
2) The Establishment of Master Plan for Consumer Policy
The provisions for the establishment of Master Plan were added to the Framework Act to set up a mid- and long-term Master Plan for Consumer Policy. The master plan is established every three years with the purpose of implementing consumer policies in a systematic and consistent manner. The latest Master Plan was established in October 2017 for the years 2018 to 2020.
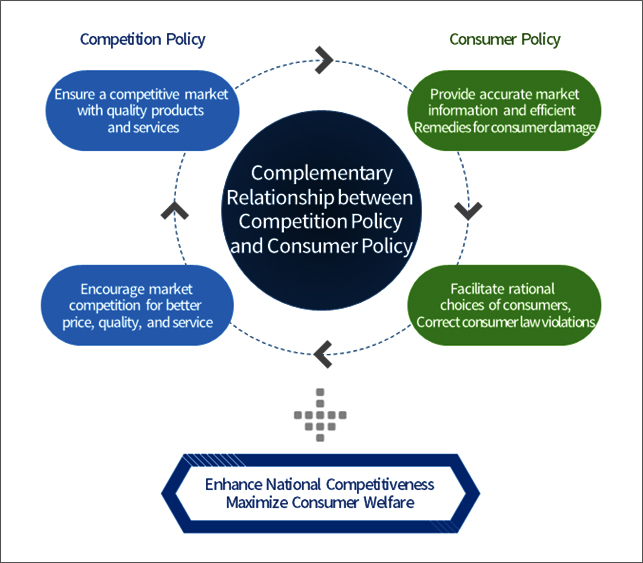
Relationship Between Competition Policy and Consumer Policy
Both competition policy and consumer policy deals with the “market” and have the ultimate goal of increasing “consumer welfare,” thus they are closely related. The unified implementation system for consumer policies allows the KFTC to effectively implement both competition policies and consumer policies.
Complementary Relationship between Competition Policy and Consumer Policy
Legislation
The Framework Act on Consumers
The Framework Act prescribes rights and duties of consumers, who are the main constituents of the free market economy, and serves as the basis for comprehensively facilitating consumer policies.
- The Framework Act prescribes ① the rights and duties of consumers, the state and business entities; ② legal basis for the establishment of the KCA and consumer organizations; ③ and detailed consumer protection measures, such as the collection of product recall information and the information on dangers and injuries; remedies for consumer damage; and dispute mediation.
The Consumer Cooperatives Act
The purpose of the Consumer Cooperatives Act is to promote independent activities of consumers in cooperatives through provisions on the admission and qualification for membership, procedure for establishment, types of business services which can be provided by the cooperatives, supervision, legal basis for the establishment of the federation of consumer cooperatives and the national federation of consumer cooperatives.
- The purpose of a consumer cooperative is to improve the welfare and livelihood of cooperative members. A consumer cooperative is a self supporting organization which provides services below:
- ① Purchase, manufacture, process and provide commodities necessary for the members;
- ② Provide services necessary for the members.
-
There are consumer cooperatives, such as cooperatives specialized in the distribution of eco-friendly agricultural
products, university consumer cooperatives (operate restaurants and cafeterias in universities), medical consumer
cooperatives (operate medical treatment and preventive healthcare services).
- There are 487 consumer cooperatives, 1.56 million cooperative members, total sales of 809 billion won (as of the end of 2018).
Key tasks
Organizing the Consumer Policy Committee (“the Committee”)
At the Committee meeting, presided by the Prime Minister, the members deliberate and decide a fundamental policy concerning the enhancement of consumers' rights and interests and the improvement of consumers' lives.
- The Committee develops the Framework Plans on Consumer Policies every three years; and formulates a comprehensive implementation plan for the Framework Plans every year by putting together and adjusting central administrative agency implementation plans and City/Do implementation plans.
- The Committee conducts ‘the Evaluation of the Consumer Orientation of Policies’ which comprises of evaluating policies and recommending necessary measures to relevant ministries to enhance consumer rights and interests.
Managing Consumer Centered Management(CCM) Certification
The KFTC grant Consumer Centered Management Certification to business entities who conduct customer-oriented management in the entire process of planning, production, and distribution of products (182 businesses are certified as of May, 2020). The KFTC provides reward and support to certified businesses and the businesses can mark such certification.
The purpose of the certification program is to lead businesses to voluntarily mediate consumer complaints and damage by setting up processes and systems for addressing consumer issues.

Setting the Regulations on Consumer Dispute Resolution
The Regulations on Consumer Dispute Resolution provide the criteria for the settlement of consumer disputes, such as repair, exchange, refund, compensation issues. The criteria shall be the criteria for any agreement or recommendation on the settlement of disputes, unless there is any separate manifestation as to the method of dispute settlement between the parties in dispute.
The criteria is used by many businesses as the criteria for after sales service and compensation for consumer damage. Also the KCA is using the criteria for consumer dispute resolution, thus the criteria has proven effective even if it is a non-mandatory provision.
Implementing Consumer Damage Prevention Measures, such as Enhanced Consumer Access to Information
The KFTC compares the quality and performance of different products and services; provides price information of new products and services, and those that have a large price discrepancy between overseas markets and Korean market.
The KFTC hires ordinary consumers to monitor consumer law violations, such as exaggerated Ads by private academies; failure to disclose material connection between an endorser and an advertise in social media, through real time field monitoring.
The KFTC provides financial support to consumer organizations for gathering victims for group litigations.
Holding Consumer Policy Events and Participating in International Meetings
The KFTC holds Consumer Rights Day (Dec. 3rd) celebration event to promote consumer rights and interests and recognize individuals and organizations for their contribution.
The KFTC organizes the Asian Forum on Consumer Policy biennially to discuss consumer related issues and policies.
The KFTC participates regularly in the OECD Committee on Consumer Policy (CCP), the OECD Working Party on Consumer Product Safety (WPCPS), the International Consumer Protection and Enforcement Network (ICPEN), and the International Consumer Product Health and Safety Organization (ICPHSO) meetings to analyze international consumer policy trends and ways to implement those trends into policies in Korea.
